visual anatomy and physiology lab manual
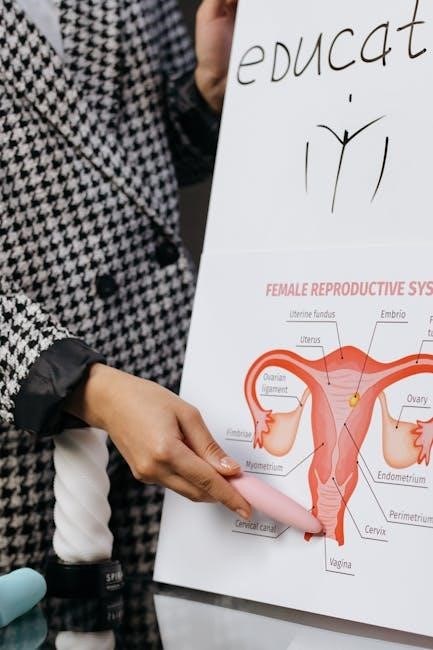
This lab manual serves as a comprehensive guide for visual exploration of anatomy and physiology. It integrates microscopy, digital imaging, and 3D models to enhance understanding. Practical exercises bridge theoretical concepts with hands-on experiences, fostering deeper comprehension of human structures and functions.
1.1 Overview of the Lab Manual
This lab manual provides a structured approach to visual learning, combining microscopy, digital imaging, and 3D models. It includes hands-on exercises, histological analyses, and practical techniques to enhance understanding of anatomical structures and physiological processes. Designed for students, the manual supports lab-based exploration, fostering engagement and retention through interactive and immersive learning experiences. It aligns with course objectives, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy and physiology.
1.2 Importance of Visual Learning in Anatomy and Physiology
Visual learning enhances comprehension of complex anatomical structures and physiological processes. Tools like microscopy, 3D models, and digital imaging provide interactive experiences, improving retention and understanding. Visual aids bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, enabling students to better grasp spatial relationships and functional mechanisms. This approach supports engagement and active learning, making anatomy and physiology more accessible and memorable for students.
1.3 Learning Objectives and Outcomes
This lab manual aims to enhance students’ understanding of anatomical structures and physiological processes. Key objectives include identifying tissues, cells, and organs, and understanding their functions. Students will master microscopy, histological analysis, and digital tools to visualize complex systems. Practical exercises will develop critical thinking and scientific inquiry skills. Upon completion, learners will demonstrate proficiency in lab techniques, data interpretation, and the application of anatomical and physiological principles to real-world scenarios, preparing them for advanced studies and professional careers.
Essential Visual Tools for Anatomy and Physiology
Microscopy, digital imaging, and 3D models are core tools for visualizing anatomical structures. These resources enhance understanding of complex systems, aiding in detailed analysis and practical applications.
2.1 Microscopy and Histological Slides
Microscopy and histological slides are fundamental tools for studying anatomy and physiology. They allow detailed examination of tissue structures, enabling identification of cellular components and their organization. Histological slides, prepared using staining techniques, reveal microscopic details essential for understanding tissue functions and pathological conditions. These resources are invaluable for both educational and research purposes, providing a visual foundation for comprehension of complex biological processes.
2.2 Digital Imaging and Software for Anatomy
Digital imaging and software tools enhance the study of anatomy by providing interactive and detailed visualizations. Platforms like the Xper Information Management System enable data acquisition, visualization, and analysis. These tools support virtual dissections, 3D reconstructions, and real-time exploration of anatomical structures. They are invaluable for both educational and research purposes, offering a modern approach to understanding complex anatomical systems.
2.3 3D Models and Virtual Dissection Tools
3D models and virtual dissection tools revolutionize anatomy education by providing interactive, three-dimensional representations of anatomical structures. Students can explore complex systems through detailed visuals, enhancing their understanding. Virtual dissections simulate real procedures, allowing practice without physical specimens. These tools promote deeper engagement and improved retention of anatomical knowledge.
Histology and Cellular Biology
Histology and cellular biology focus on the microscopic study of tissues and cells, essential for understanding anatomical structures. Microscopy and staining techniques reveal cellular details, aiding in practical lab exercises.
3.1 Types of Tissues and Their Functions
The human body is composed of four primary tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Each plays a distinct role in maintaining bodily functions. Epithelial tissues form barriers and linings, while connective tissues provide support and structure. Muscle tissues enable movement through contraction, and nervous tissues facilitate communication via nerve impulses. Understanding these tissue types is crucial for visual anatomy and physiology studies, as they form the foundation of organ systems and their functional processes.
3.2 Cellular Structure and Organelles
The cell is the fundamental unit of life, consisting of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and organelles like mitochondria, ribosomes, and the nucleus. Mitochondria generate energy through ATP production, while ribosomes synthesize proteins essential for cellular function. The nucleus houses genetic material, regulating cell activities. Other organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, and Golgi apparatus, play roles in protein processing, digestion, and transport. Studying these structures visually aids in understanding cellular processes and their importance in anatomy and physiology.
3.3 Staining Techniques for Microscopic Analysis
Staining techniques enhance microscopic observations by highlighting structural details. Common methods include hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for general tissue examination, while specialized stains target specific structures. These techniques improve contrast, aiding in the identification of cellular components and histological features. Proper staining protocols are essential for accurate analysis, ensuring clear visualization of samples under microscopy. This step is critical for understanding tissue composition and diagnosing conditions, making it a cornerstone of anatomy and physiology labs.

Organ Systems Overview
This section explores the integration of visual tools and practical exercises to examine the structure and function of major organ systems, enhancing anatomical understanding through hands-on learning.
4.1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems
This section focuses on the visual exploration of the skeletal and muscular systems, utilizing 3D models and microscopy to examine bone structure, muscle fibers, and their functional relationships. Practical exercises include identifying anatomical landmarks on dissected specimens and analyzing the role of muscles in movement. The integration of digital imaging tools enhances understanding of how these systems contribute to overall body mechanics and support. Lab activities emphasize hands-on learning to correlate structure with function, reinforcing key physiological concepts.
4.2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
This section visually explores the circulatory and respiratory systems, focusing on their interconnected roles in oxygenation and nutrient delivery. Using microscopy, students examine blood cells and vascular tissues, while digital imaging highlights organ structures like the heart and lungs. Practical exercises include simulating gas exchange and measuring blood pressure, correlating visual observations with physiological functions. These activities reinforce the importance of these systems in maintaining homeostasis and overall bodily functions, emphasizing their interdependence in supporting life.
4.3 Nervous and Digestive Systems
This section delves into the nervous and digestive systems, emphasizing their roles in communication and nutrient processing. Visual tools like microscopy reveal neural structures, while 3D models illustrate digestive pathways. Practical exercises include observing nerve reflexes and simulating enzymatic digestion. These activities help students correlate anatomical features with physiological functions, such as neural signaling and nutrient absorption, providing a clear understanding of how these systems interact to sustain bodily functions and maintain overall health.
Physiology of Body Systems
This chapter explores the physiological processes of major body systems, focusing on the nervous, circulatory, and digestive systems. Visual tools and interactive exercises allow students to examine how these systems function, regulate, and interact to maintain homeostasis. Practical observations and simulations enhance understanding of processes like neural signaling, blood circulation, and nutrient absorption, providing a dynamic approach to learning complex physiological concepts.
5.1 Nervous System Function and Reflexes
This section delves into the nervous system’s role in controlling bodily functions, emphasizing neural signaling and reflex mechanisms. Visual aids like 3D models and interactive simulations illustrate how neurons transmit signals. Practical exercises allow students to observe reflex actions, such as knee-jerk responses, and understand the brain-spinal cord interaction. These tools enhance comprehension of the nervous system’s complexity and its essential role in maintaining homeostasis and enabling voluntary and involuntary actions.
5.2 Blood Circulation and Gas Exchange
Blood circulation and gas exchange are vital for delivering oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. The heart pumps blood through arteries and veins, while the lungs facilitate gas exchange in the alveoli. Visual tools like 3D models and interactive simulations provide detailed views of these processes. Practical exercises include observing blood flow through microscopes and measuring physiological parameters like heart rate and blood pressure. These activities help students understand the dynamic nature of circulatory and respiratory systems in maintaining homeostasis.
5.3 Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
Digestion involves breaking down food into nutrients through mechanical and chemical processes. The mouth and stomach initiate this process, while the small intestine absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream. Visual tools like 3D models of the digestive tract and virtual simulations of enzymatic reactions enhance understanding; Lab exercises include observing histological slides of intestinal lining and measuring pH levels in digestive fluids; These activities provide hands-on insights into how the body processes and utilizes nutrients for energy and growth.
Practical Lab Exercises
Practical lab exercises involve hands-on activities like dissections, physiological measurements, and experimental setups. These exercises reinforce visual learning and provide real-world applications of anatomical and physiological concepts.
6.1 Dissection Techniques and Safety
Dissection techniques require precision and care to ensure accurate anatomical exploration. Proper handling of instruments and tools is emphasized to maintain safety. Safety protocols include wearing personal protective equipment and following lab guidelines to prevent accidents. Students are trained in best practices for specimen preparation, dissection, and cleanup. Emphasis is placed on adhering to lab rules and procedures to create a safe learning environment while gaining hands-on experience with anatomical structures.
6.2 Measuring Physiological Parameters
Measuring physiological parameters involves using tools like stethoscopes, blood pressure cuffs, and spirometers to assess heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory function. Students learn to collect accurate data using proper techniques. These exercises help understand the body’s functional responses and integrate visual observations with numerical data. Digital tools and software enhance data analysis. Safety and precision are emphasized to ensure reliable results and proper handling of equipment. This hands-on approach connects theoretical knowledge with real-world applications in health and physiology.
6.3 Experimental Design and Data Analysis
Experimental design involves creating structured hypotheses and controlled variables to investigate anatomical and physiological phenomena. Students learn to collect and analyze data using various tools and techniques. Digital software aids in visualizing and interpreting results, enhancing understanding of complex biological processes. Emphasis is placed on accurate documentation and reproducibility. This section teaches critical thinking and scientific methodology, preparing students to design and execute experiments effectively while drawing meaningful conclusions from their findings in anatomy and physiology studies.

Assessment and Evaluation
Assessment involves grading lab work, reports, and participation. Feedback mechanisms help improve understanding and skills, ensuring students meet learning objectives effectively throughout the course.
7.1 Grading Criteria for Lab Work
Lab work is graded based on accuracy, completeness, and understanding of anatomical structures and physiological processes. Participation, lab reports, and adherence to safety protocols are also evaluated. Grading emphasizes clear documentation and correct identification of specimens or digital models. Timely submission of assignments and engagement in discussions contribute to the final score. Feedback is provided to help students improve their skills and meet course objectives effectively.
7.2 Lab Reports and Presentation Guidelines
Lab reports must include clear observations, accurate data, and proper documentation of procedures. They should follow a structured format with an introduction, methods, results, and discussion. Presentations require students to demonstrate understanding of anatomical and physiological concepts visually. Proper formatting, use of visual aids, and adherence to submission deadlines are mandatory. Students are encouraged to seek feedback from instructors to refine their reports and presentation skills, ensuring clarity and precision in communicating scientific findings.
7.3 Feedback Mechanisms for Improvement
Feedback is provided through detailed evaluations of lab reports and presentations, ensuring students understand their strengths and areas for improvement. Instructors offer constructive comments to enhance learning outcomes. Peer reviews and self-assessment tools are also utilized to foster reflective learning. Students are encouraged to incorporate feedback into revised submissions, promoting academic growth and mastery of anatomical and physiological concepts.

Resources and References
This section provides a curated list of textbooks, online materials, and safety protocols essential for visual anatomy and physiology learning, ensuring comprehensive academic support and laboratory preparation.
8.1 Recommended Textbooks and Online Materials
Essential resources include textbooks like The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Anatomy & Physiology and Anatomy & Physiology for Dummies. Online platforms offer interactive tools, such as virtual dissection software and 3D anatomy models. Additionally, course materials like BI 425 provide detailed lab guides and visual aids for enhanced learning. These resources support both theoretical understanding and practical application, ensuring a well-rounded education in visual anatomy and physiology.
8.2 Lab Safety Guidelines and Protocols
Lab safety is paramount, requiring strict adherence to protocols. Students must wear PPE, handle chemicals with care, and use dissection tools safely. Proper waste disposal and emergency procedures are emphasized. Regular training ensures awareness of potential hazards. Violations of safety guidelines may result in disciplinary action, as outlined in the lab manual. Compliance is mandatory to protect individuals and maintain a secure learning environment.
8.3 Additional Visual Aids for Enhanced Learning
Supplemental visual tools like 3D animations, virtual simulations, and interactive diagrams enhance comprehension. Digital imaging software allows students to explore microscopic structures in detail. Virtual dissection tools provide immersive experiences, enabling students to examine anatomical layers. Additionally, comparative anatomy resources and physiology simulations offer practical insights. These aids bridge gaps between textbook content and real-world applications, fostering a deeper understanding of complex anatomical and physiological concepts through interactive and engaging methods.