teeth parents guide

This guide provides essential information for parents to promote healthy dental habits in children. It covers when to start brushing, choosing the right tools, and effective techniques.
Why Dental Health Matters for Children
Maintaining dental health is crucial for children’s overall well-being. Poor dental hygiene can lead to tooth decay, pain, and self-esteem issues. Healthy teeth promote proper chewing, speaking, and confidence. Good habits from an early age prevent long-term problems. This guide helps parents understand the importance of dental care and provides practical advice to ensure their children’s teeth remain healthy and strong.
Key Statistics on Children’s Dental Health
Nearly half of U.S. children experience decay, fillings, or missing teeth by age 9. Early brushing is crucial, starting with the first tooth. Children’s toothpaste, with optimal fluoride, is recommended. Tooth decay is a common issue, affecting many youngsters. Regular dental care helps prevent these problems. Parents should prioritize daily brushing and proper oral hygiene to safeguard their child’s dental health from an early age.
Overview of the Guide
This comprehensive guide empowers parents with knowledge to foster healthy teeth in children. It covers oral hygiene practices, diet, and common dental issues, while addressing developmental milestones and environmental influences. The guide also outlines the importance of regular dental visits and how to handle emergencies. Whether you’re a new parent or seeking to improve your child’s dental care, this resource provides practical advice and insights to ensure a lifetime of healthy smiles.

Oral Hygiene Practices for Kids
This section introduces oral hygiene practices, emphasizing early brushing, proper toothbrush selection, and effective cleaning techniques to maintain children’s dental health and prevent issues.
When to Start Brushing Your Child’s Teeth
Start brushing your child’s teeth as soon as the first tooth appears, typically around 6 months old. Use a soft baby toothbrush and a smear of children’s toothpaste. Early brushing helps prevent decay, promotes healthy gums, and establishes a daily routine. Continue brushing twice a day as more teeth erupt. This practice lays the foundation for lifelong oral hygiene and ensures your child’s teeth develop healthily from the very beginning.
Choosing the Right Toothbrush and Toothpaste
For children, choose a toothbrush with soft bristles and a small head to gently clean emerging teeth. Opt for a child-sized handle for better grip. Use children’s toothpaste with fluoride, as it strengthens enamel and prevents decay. Select a flavor your child likes to encourage brushing. Avoid adult toothpaste, which may contain too much fluoride. Replace toothbrushes every 3-4 months or when bristles fray. The right tools make brushing effective and comfortable for kids.
How to Brush Effectively
Brushing should start as soon as the first tooth appears. Use gentle circular motions to cover all surfaces, focusing on the front, back, and top teeth. Ensure the bristles reach the gum line without scrubbing too hard. Pay special attention to areas where teeth and gums meet. Brush for two full minutes, twice daily, to remove plaque and food particles. Demonstrate the technique and let your child mimic you. Make it a positive experience to encourage consistency and develop good oral hygiene habits from an early age.
Diet and Nutrition for Healthy Teeth
A balanced diet is crucial for healthy teeth. Limit sugary foods and drinks to reduce cavity risks. Encourage fruits, vegetables, and calcium-rich foods to support strong enamel development.
The Role of Sugar and Cavities
Sugar plays a significant role in the development of cavities in children. When sugar is consumed, bacteria in the mouth produce acid, which erodes tooth enamel. Frequent exposure to sugary snacks and drinks increases cavity risks. Parents should limit sugary foods and encourage water intake to rinse the mouth. Additionally, balancing sugar intake with fluoride toothpaste can help protect teeth. Monitoring sugar consumption is essential for preventing decay and promoting long-term dental health.
Best Foods for Dental Health
Encouraging a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products supports healthy teeth. Foods high in fiber, like apples and carrots, stimulate saliva production, naturally cleaning teeth. Dairy products, such as milk and cheese, provide calcium and minerals that strengthen enamel. Water is essential for hydration and rinsing food particles. Nuts and seeds can help clean teeth naturally, while whole grains offer nutrients for overall dental well-being. Incorporating these foods into meals helps prevent decay and promotes a healthy smile.

Common Dental Issues in Children
Common dental issues in children include tooth decay, cavities, and gum inflammation. Regular brushing, fluoride, and check-ups help prevent these problems and maintain healthy gums and teeth.
Tooth Decay and Fillings
Tooth decay is a common issue in children, often caused by poor oral hygiene and sugary diets. Early signs include white spots on teeth, which can progress to cavities if untreated. Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste and dental check-ups can prevent decay. When cavities form, fillings are necessary to restore teeth and prevent further damage. Parents should encourage healthy habits and monitor their child’s dental health to avoid more severe problems. Prompt treatment ensures teeth remain strong and functional. Regular fluoride exposure is key to protecting enamel and preventing decay.
Lost or Missing Teeth
Children typically begin losing baby teeth around age 6, starting with the front teeth, resulting in the characteristic “gappy” smile. This natural process makes way for permanent teeth. Losing teeth is usually painless, but some children may experience mild discomfort or bleeding. Parents should reassure their child and monitor the process. If a tooth is lost due to injury or falls out prematurely, consult a dentist. Lost teeth are a normal part of dental development, and most children lose all baby teeth by age 12 or 13, making way for a healthy, permanent smile.

Developmental Milestones
Children typically lose baby teeth around age 6, starting with front teeth, and usually lose all by age 12 or 13, making way for permanent teeth.
When Baby Teeth Appear
Baby teeth typically begin to appear when a child is around 6 months old, with the front teeth usually coming in first. By age 3, most children have a full set of 20 baby teeth. Parents should start brushing as soon as the first tooth emerges to establish good oral hygiene habits early. Monitoring teething symptoms and maintaining proper care helps ensure healthy development and prevents early dental issues. Regular check-ups with a pediatric dentist are also crucial during this stage.
When Baby Teeth Fall Out

Children typically begin losing baby teeth around the age of six, starting with the front teeth, which creates the familiar “gappy smile.” By age 12, most baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. The process usually progresses naturally, but parents should monitor it to ensure proper alignment and development. If a child loses a tooth prematurely due to injury or decay, consulting a dentist is advised to prevent future dental issues. Regular check-ups help track the progress and address any concerns early on.

Factors Influencing Dental Health
Genetic and medical conditions can influence tooth development, while environmental factors like diet and hygiene practices significantly impact dental health in children.
Genetic and Medical Conditions
Genetic factors, such as enamel hypoplasia or cleft palate, can affect tooth development. Medical conditions like cerebral palsy or Down syndrome may also impact dental health. These conditions often require specialized care. Parents should consult pediatric dentists to address unique needs. Early intervention is key to managing genetic or medical influences on dental health. Regular monitoring and tailored treatments, such as fluoride applications or dietary adjustments, can help mitigate potential issues. Understanding these factors helps parents provide better care for their child’s teeth.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors significantly impact a child’s dental health. Access to clean water, fluoride exposure, and socioeconomic status play roles in preventing cavities. Children in areas with fluoridated water often have fewer cavities. Socioeconomic factors can influence dietary habits and access to dental care. Parents should minimize sugary snacks and ensure proper oral hygiene. Environmental conditions, such as exposure to secondhand smoke, can also affect gum health. Understanding these factors helps parents create a healthier environment for their child’s teeth. Regular dental check-ups can address environmental influences early on.
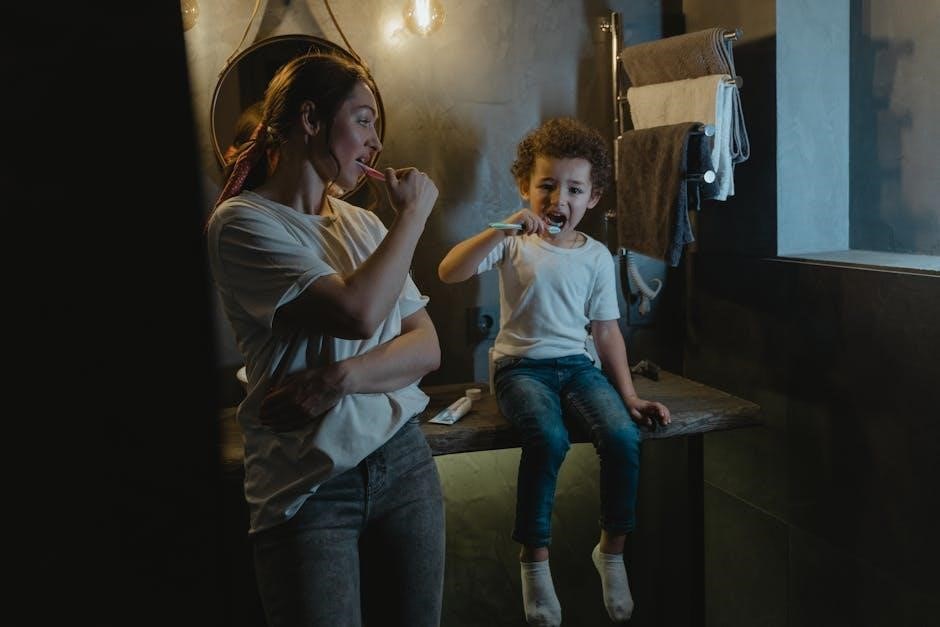

Dental Visits and Check-Ups
Regular dental visits are crucial for early detection and prevention of oral issues. Schedule the first visit by age one or when the first tooth appears.

When to Schedule the First Dental Visit
The first dental visit should occur when the first tooth appears or by the child’s first birthday. Early visits help prevent potential issues, allow the dentist to monitor tooth development, and provide guidance on proper oral care. This initial check-up is a great opportunity to address any concerns and set the foundation for lifelong dental health. It’s a gentle examination with personalized advice, ensuring parents are equipped to support their child’s oral well-being effectively.
What to Expect During a Child’s Dental Check-Up
A child’s dental check-up involves a gentle examination of their teeth and gums to assess oral health. The dentist will look for signs of decay, check gum health, and monitor tooth development. They may also clean the teeth gently and apply fluoride if needed. Parents can expect personalized advice on brushing, diet, and preventive care. The visit is designed to be positive and reassuring, helping children feel comfortable with dental care while addressing any concerns and promoting a healthy smile from an early age.

Dental Emergencies
Dental emergencies, such as a lost tooth, require staying calm. Assess the situation, rinse the tooth with water if possible, and contact a dentist immediately for guidance.
What to Do If a Child Loses a Tooth
If a child loses a tooth, remain calm and assess the situation; Gently rinse the tooth with water if possible, avoiding scrubbing. Store it in a clean container or cheek to keep it moist. Contact a dentist immediately for guidance, as they may recommend reimplantation or further evaluation. Lost baby teeth typically don’t require reimplantation, but permanent teeth do. Stay reassuring to help the child feel comfortable and understand it’s a natural part of dental development.